چسبهای مهندسی میتوانند به روشهای مختلف دستهبندی شوند:
گروه شیمیایی: اپوکسی، فنولیک، اورتان، بیهوازی، اکرلیک، سیانو اکرلایت، سیلیکون و پلی سولفید اصلیترین آنها هستند
نوع عمل: سازهای، ذوب گرم، حساس به فشار و مشابه آن
شکل فیزیکی قبل از پخت: یک یا دو جزئی، مایع، نوار، خمیر، جامد
شکل فیزیکی بعد از پخت: صلب یا انعطافپذیر
فرآیند پخت: پیوند عرضی، پلیمریزاسیون
نحوه پخت: گرما، نور UV، اشعه الکترونی، رطوبت و مشابه آن
حالت پخته: ترموست یا ترموپلاستیک
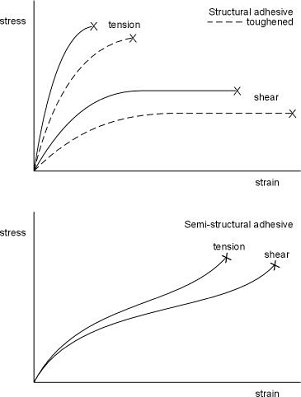
صلبیت چسب پختهشده اثری ویژه روی توزیع تنشها در یک اتصال دارد. خواص کششی و برشی یک اپوکسی سازهای صلب با یپلی اروتان منعطف در شکل زیر مقایسه شده است، که از آن میتوان نکات ذیل را دریافت.
– اپوکسی سازهای در ماهیت، شیشهای است در حالیکه پلی اروتان ماهیتی لاستیکی دارد.
– برای اپوکسی سازهای، مدول اولیه بالا است و سپس (قبل از شکست) تسلیم اتفاق میافتد. استحکام در کشش بالاتر از برش است، اما آنچه باعث میشود که اتصال به تنشهای پیلینگ حساس باشد، کرنش تا شکست است.
– چقرمهسازی اپوکسی سازهای باعث کاهش استحکام تسلیم میشود و کرنش تا شکست را افزایش میدهد، که نتیجه آن کاهش حساسیت به تنشهای پیلینگ است.
– مقدار مدول برای پلی اورتانها حدود ۱۰۰ الی هزار برابر کمتر از مدول کرنشآهسته اپوکسیهای سازهای است.
– برای پلی اروتانها در هر دو حالت کشش و برش، کرنش تا شکست بالایی بهدست میآید، آنقدر که شکست اتصال به تنشهای پیلینگ حساس نخواهد بود.
برای روشن شدن محدوده خواص چسبها، جزئیات سه نوع شیمیایی (اپوکسی، اکرلیک، و پلیاورتانها) را بررسی میکنیم. خواص عمده این چسبها در ذیل آورده شده است. بالاترین دمای کاری (UST)، دمایی است که استحکام چسب به ۵۰ درصد استحکام خود در دمای اتاق افت میکند. برای چسبهای ترموست مانند اپوکسیها و اکرلیکها، این دما تابع دمای انتقال به شیشه چسب است.
گروه اپوکسی
چسبهای سازهای، مدول بالا، پخت آهسته (مگر اینکه گرم شوند)، با دوام
چسبهای یک جزئی: مدول برشی ۲ تا ۵/۳ گیگا پاسگال، حد الاستیک ۴۰ مگا پاسگال، UST در ۱۲۰ درجه سانتیگراد، و درز اتصال کمتر از ۲ میلیمتر
چسبهای دو جزئی: مدول برشی ۲/۰ تا ۰/۱ گیگا پاسگال، حد الاستیک ۲۵ مگا پاسگال، UST در ۵۰ درجه سانتیگراد، و درز اتصال کمتر از ۲ میلیمتر
اپوکسیهای تکجزئی از قبل کاتالیزه شدهاند و برای پلیمریزاسیون نیاز به حرارت دارند، که بعد از آن یک پلیمر ترموست تشکیل میدهند که قابلیت ذوب مجدد با حرارتدهی ندارد. معمولاً استحکام همبستگی بالایی دارد و افزدون یک فاز لاستیکی باعث افزایش چقرمگی و بهبود مقاومت به شکست و خستگی آن میشود (با مکانیزم کور کردن نوک ترک). اپوکسیهایی که با گرما پخت میشوند این مزیت را نیز دارند که میتوانند لایه چربی روی سطح را از بین ببرند. رفتار رئولوژیکی میتواند از مایع با گرانروی کم تا خمیر صلب متغیر باشد.
سیستمهای دو جزئی (۲k) معمولاً در دمای اتاق پخت میشوند، و در جایی مناسب هستند که امکان حرارتدهی وجود ندارد. با انتخاب مناسب نوع رزین-هاردنر و نسبت اختلاط میتوان خواص مکانیکی متفاوتی بهدست آورد. اگرچه دوام اپوکسیهای ۲k به خوبی اپوکسیهای با پخت حرارتی نیست، پیشرفتهای اخیر آنها را برای کاربردهای سازهای مناسب کردهاست.
اپوکسیها با اکثر مواد سازگار هستند، با این حال، چسبیدن آنها به ترموپلاستیکها و لاستیکها میتواند مشکل باشد. پلیمرهای با انرژی سطحی پایین (پلی اولفینها و فلورو پلیمرها) اتصال را مشکل میکنند و نیاز به پیشعملیات سطحی است.
کاربردهای اصلی این چسبها در اجزای فضاپیماها، خودروها و صنایع ساخت و ساز است.
گروه اکرلیک
چسبهای نیمهسازهای، نسبتاً انعطافپذیر، پخت سریع، بادوام
چسبهای یک یا دو جزئی: مدول ۱/۰ تا ۴/۰ گیگا پاسگال، حد الاستیک ۵ مگا پاسگال، UST در ۸۰ تا ۱۵۰ درجه سانتیگراد، درز اتصال کمتر از ۵/۰ میلیمتر
سه نوع اصلی از چسبهای اکرلیک وجود دارد؛
بیهوازی: پخت در غیاب هوا و در تماس با مس یا آهن. این نوع چسبها بالاترین دمای کاری را دارند ( تا ۱۵۰ درجه سانتیگراد) و معمولاً برای کاربردهای آببندی یا قفلکننده رزوه استفاده میشود.
سیانواکرلایت: این نوع چسب در دمای اتاق و در تماس با عاملهای آلکالین (موجود در بخار هوا) بهسرعت پخت میشود و میتوان اتصالی قوی در فلزات، پلاستیکها و لاستیکها ایجاد کند. برای کاربردهای با بارگذاری بالا مناسب نیستند. دمای کاری آنها با حفظ قابلتوجه استحکام به حدود ۸۰ درجه سانتیگراد میرسد.
چقرمهشده: معمولاً دو جزئی هستند و بسته به نسبت اختلاط، شرایط پخت متفاوتی دارند. انواع مختلف آمادهسازی سطح میتواند استفاده شود. اکثر مواد بهخصوص فلزات را خوب میچسباند اما برای لاستیکها و پلیمرهای کماصطکاک کارایی خوبی ندارد. دمای کاری میتواند به حدود ۱۲۰ درجه برسد.
گروه پلی اروتان
نیمهسازهای، انعطافپذیر، نرخ پخت قابل کنترل، دوام کم، بهصورت خمیر
چسبهای یگ یا دو جزئی: مدول برشی ۰۵/۰ تا ۲/۰ گیگاپاسگال، حد الاستیک ۵ مگا پاسگال، UST در ۱۰۰ درجه سانتیگراد، درز اتصال کمتر از ۴۰ میلیمتر
نیمهسازهای، پخت سریع در دمای محیط، چسبهایی که انعطافپذیر هستند و میتوانند برای هر دو کاربرد آببندی و چسباندن استفاده شوند. زمانی که درز اتصال بزرگ است، پلی اورتانها (PU) میتوانند با اضافه کردن عاملهای فومی مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. این چسبها برای مواد مختلفی از جمله فلز، پلاستیک، لاستیک و شیشه استفاده شود.
یکی از موانع استفاده از چسبهای PU حساسیت آنها به رطوبت (چه قبل و چه بعد از پخت) است. رنگآمیزی سطوحِ فلز قبل از اعمال چسب میتواند کمک کند. پرهیز از اعمال نیروی بالا در محیطهای مرطوب توصیه شدهاست.
پیشرفتهای اخیر در چسبهای ترکیبی پلیاورتان-اپوکسی، موادی را حاصل کرده است که میتوانند مقاومتر باشند. این چسبها اولین بار برای صنعت خودرو توسعه یافتند.
Adhesives for engineering use may be classified in various ways:
- Chemical group – the main ones being epoxy, phenolic, urethane, anaerobic, acrylic, cyanoacrylate, silicone and polysulphide
- Functional type – structural, hot melt, pressure sensitive etc
- Physical form before curing – 1 or 2 part, liquid, film, paste, solid
- Physical form after curing – rigid or flexible
- Curing process – cross-linking, polymerisation,
- Curing method – heat, UV light, electron beam, moisture etc
- Cured state -Thermoplastic or thermoset
The rigidity of the cured adhesive has a significant effect on the stress distribution in a joint. The tensile and shear properties of a rigid structural epoxy are compared to a flexible polyurethane in the Figure below from which the following can be noted.
- The structural epoxy is glassy in nature whilst the polyurethane is rubbery in nature.
- For the structural epoxy, the initial modulus is high and then yielding occurs prior to failure. The strength is higher in tension than in shear, but the strain to failure which is the reason for joint failure to be susceptible to peel stresses.
- Toughening of the the structural epoxy reduces the yield stresses and increases the strains to failure, reducing the susceptibility to failure from peel stresses.
- The modulus values for the polyurethane is 100 to 1000 times lower than the low strain modulus values of the structural epoxy.
- For the polyurethane a high strain to failure is obtained in both tension and shear so that joint failure is insensitive to peel stresses.

Details of three chemical types (epoxies, acrylics, and polyurethanes) of adhesive are used to illustrate the range of properties available, these are.
Typical properties are shown below. Upper service temperatures (UST) are the values where 50% of 23°C strength is retained. For thermoset adhesives like epoxies and acrylics this is governed by the glass transition temperatures of the adhesive.
Epoxy Group
Structural adhesives, high modulus, slow cure unless heated, durable
۱ part – Shear modulus 2.0-3.5 GPa Elastic limit 40 MPa UST 120°C Bond fill <2mm
۲ part – Shear modulus 0.2-1.0 GPa Elastic limit 25 MPa UST 50°C Bond fill <2mm
Single component epoxies are pre-catalysed and require the application of heat for polymerisation to occur, forming a hard thermoset polymer that will not re-melt on further heating. High cohesive strength is typical and the addition of a rubber phase will toughen the adhesive and improve its fracture and fatigue resistance, by local crack tip blunting. Certain heat curing epoxies also have the benefit of scavenging oil films, particularly useful where thin sheet adherends are coated with anti-corrosion or processing oils. The rheological form can be varied from a low viscosity liquid to a solid paste.
Two part (2k) systems are available and often cure at room temperature, making them suitable for applications where heat curing is impractical – e.g. repair shops. Different mechanical properties of the cured adhesive can be obtained by the careful selection of resin-hardener type and mix ratio. Although the durability of 2k epoxies will not be as good as their heat cured equivalents, modern developments do make them suitable for structural applications.
Epoxies are compatible with most materials, however, bonding to thermoplastics and rubbers can be difficult. Low surface energy polymers (polyolefins and fluoropolymers) make bonding difficult, and require special surface pre-treatments.
Typical applications include major structural components for the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Acrylic Group
Semi-structural adhesives, fairly flexible, fast curing, durable
۱/۲ part Shear modulus 0.1-0.4 GPa Elastic limit 5 MPa UST 80-150°C Bond fill <0.5mm
۳ main types of acrylic adhesives exist, these are:
Anaerobics – cure in absence of air and on contact with iron or copper. These have the highest operating temperatures (up to 150°C) and are typically used for tread locking and sealing applications.
Cyanoacrylates – fast room temperature curing on contact with alkaline agents (present in air vapour) to create strong bonds between metals, plastics, and rubber. Not suitable for high load bearing applications. Operating temperatures of up to 80°C can be achieved, with significant retention of strength.
Toughened – often 2-part mixes with variable cure characteristics based on mix ratios. Most tolerant adhesive type to variation in surface preparation. Bonds most materials well, in particular metals but does not work well with rubbers or low friction polymers. Operating temperatures up to 120°C can be achieved.
Polyurethane Group
Semi-structural, flexible, controllable cure rate, limited durability, pastes
۱/۲ part – Shear modulus 0.05-0.2 GPa Elastic limit 5 MPa UST 100°C Bond fill <40mm
Semi-structural, rapid room temperature curing, adhesives that are flexible and can be considered for both bonding and sealing applications. PU adhesive can be used where large gaps between adherends exist, with the addition of foaming agents within the mix. They can be used with a wide range of adherends including metals, plastics, rubbers, and glass.
The one major restraint with the PU adhesives is their susceptibility to moisture, both during and after curing. The painting of metal surfaces prior to application can help. Protection from high loads in hot humid environments should be considered.
Recent developments in epoxy-polyurethane hybrid adhesives have produced structural adhesives that make use of the PU component to improve impact resistance. These adhesives are being developed primarily for the automotive industry.
All data is provided by Lees WA, Adhesives, Section B15 Kempe’s Engineers Year-Book, 2000.